Nowadays, technologies develop so rapidly and market demands change so frequently that those who fail to follow new tendencies and adopt innovations quickly fall into oblivion.
It works the same way for software testing. Not to be labeled as old-school, QA experts need to follow new industry trends and use the latest testing technologies.
Keep your eye on our list of software testing trends in 2025 if you want to deliver excellent QA services, maintain industry leadership, and stay competitive.
Challenges facing QA teams in 2025
Let’s start with the challenges QA experts may face in 2025. First of all, this is rapid technology development. While being definitely a boon, it, on the other hand, also exposes difficulties for the QA community. Within a short period of time, testers need to master new technologies in order to test them properly or integrate them smoothly into their own workflows. The most prominent example is AI.
The AI market size is expected to grow by at least 120% year-over-year, while 83% of companies claim that AI is a top priority in their business plans.
To properly test AI solutions, QA teams must come up with new efficient techniques. Also, other cutting-edge technologies, like blockchain, big data, AR/VR, etc., should not be overlooked as well.
The shortage of skilled QA engineers is one more challenge that needs to be addressed in 2025. For instance, TSG Training says that currently in the United Kingdom, there are 25 QA engineers per 100,000 citizens, while the demand for skilled QA specialists is growing by 25% yearly. Preparing new QA professionals and upskilling the existing workforce are key steps that need to be taken. As of now, a significant skill gap is noticed in such software testing areas as automation testing, security testing, performance testing, and DevOps.
Also, in 2025, QA experts still face time constraints. 85% of managers say that it is hard to deliver innovation faster, without compromising on quality, as testing remains too time-consuming. Interestingly, 90% acknowledge that test automation scaling is the most important facet of reaching success. Therefore, QA teams strive both to increase the number of automated tests and enhance the test automation process as a whole through AI adoption.
Noteworthy, while some teams are working on fine-tuning test automation, others still struggle to adopt it efficiently. Selecting a test tool, managing test environments, and handling frequent requirement changes are the key pain points within this area.
Software testing trends for 2025
Software testing is on the mission to ensure the delivery of secure, reliable, and high-performing apps.
While using battle-tested QA methodologies and techniques is definitely helpful, it is even more important to know and be open to brand-new industry trends and tendencies.
Why? Because that’s the way to stay relevant, competitive, and innovative and deliver the desired outcomes as fast as possible. Ignoring new trends is just like navigating with a paper map in the era of GPS.
Surely, you’ll eventually reach your destination, but competitors armed with advanced tools will arrive sooner while spending less effort.
If you do not want to fall behind, take your time to familiarize yourself with key testing trends in 2025. Here we go!
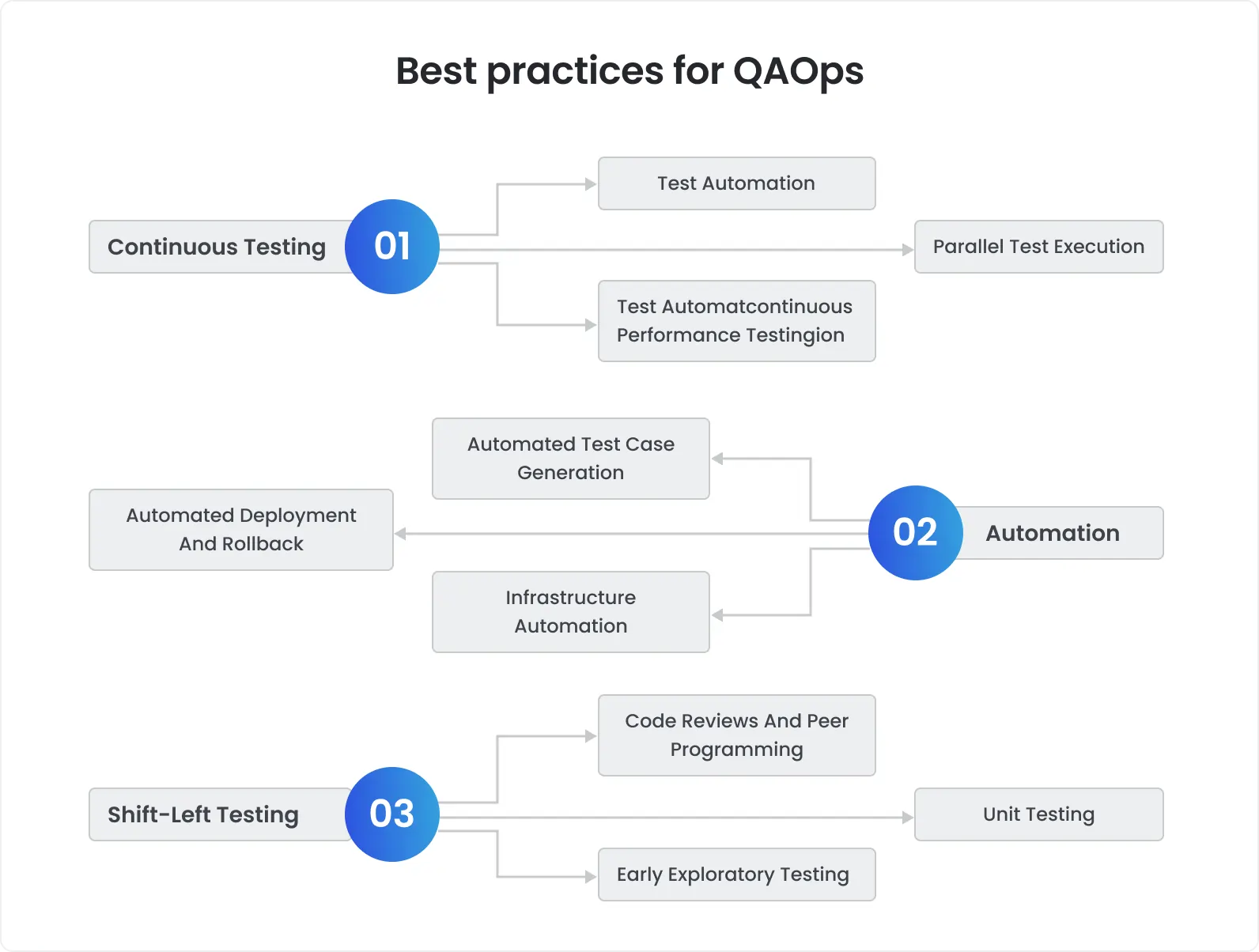
Trend 1: DevOps and QAOps integration
DevOps, a philosophy suggesting close collaboration of development and ops teams, has already proved its value by considerably improving team efficiency and speeding up software development and delivery.
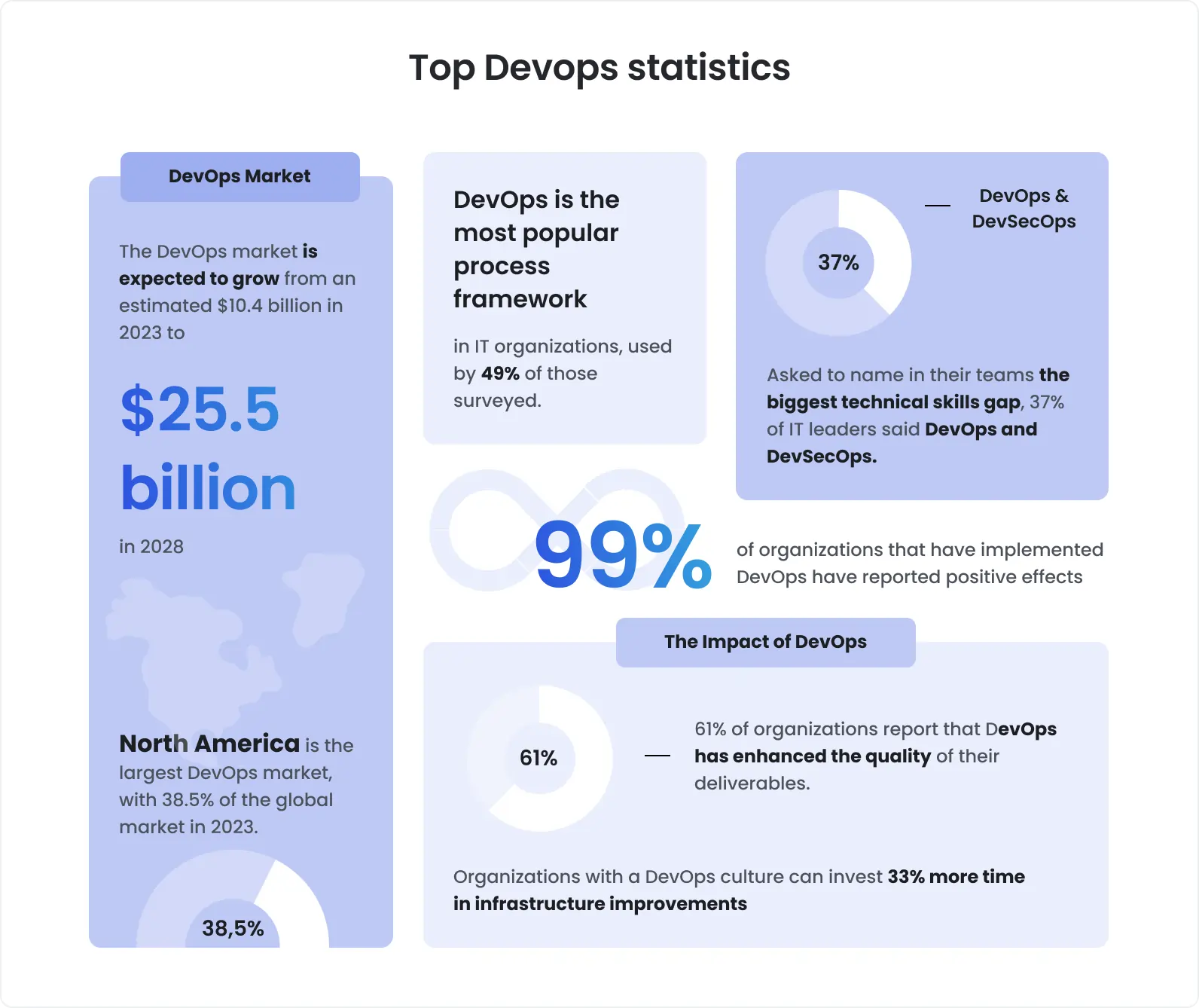
Due to the numerous benefits that DevOps brings, many teams continue to integrate its practices.
The list of key DevOps practices:
CI/CD is a cornerstone of DevOps services and solutions, as CI/CD pipelines automate the core processes of building, testing, and deployment, allowing teams to quickly and confidently deliver updates.
Infrastructure as a code (IaaC) is especially helpful since it enables automated provision and management of infrastructure, including servers, networks, VM instances, etc. All the related issues are tackled through coding rather than manually, which increases consistency and facilitates rapid scaling.
While containerization ensures consistency across environments by packaging apps with their dependencies into isolated units, i.e. containers, orchestration automates deployment, scaling, and management of these containers, providing efficient resource utilization and scalability.
DevSecOps practices as cyberattacks are getting more and more severe, more teams strive to embed robust security measures like static and dynamic code analysis, security testing, and vulnerability scans, into every phase of the DevOps pipeline.
Continuous monitoring helps teams track the performance and stability of their apps and infrastructure in real time to detect and address issues proactively. As a result, downtime is minimized, while the user experience is improved.
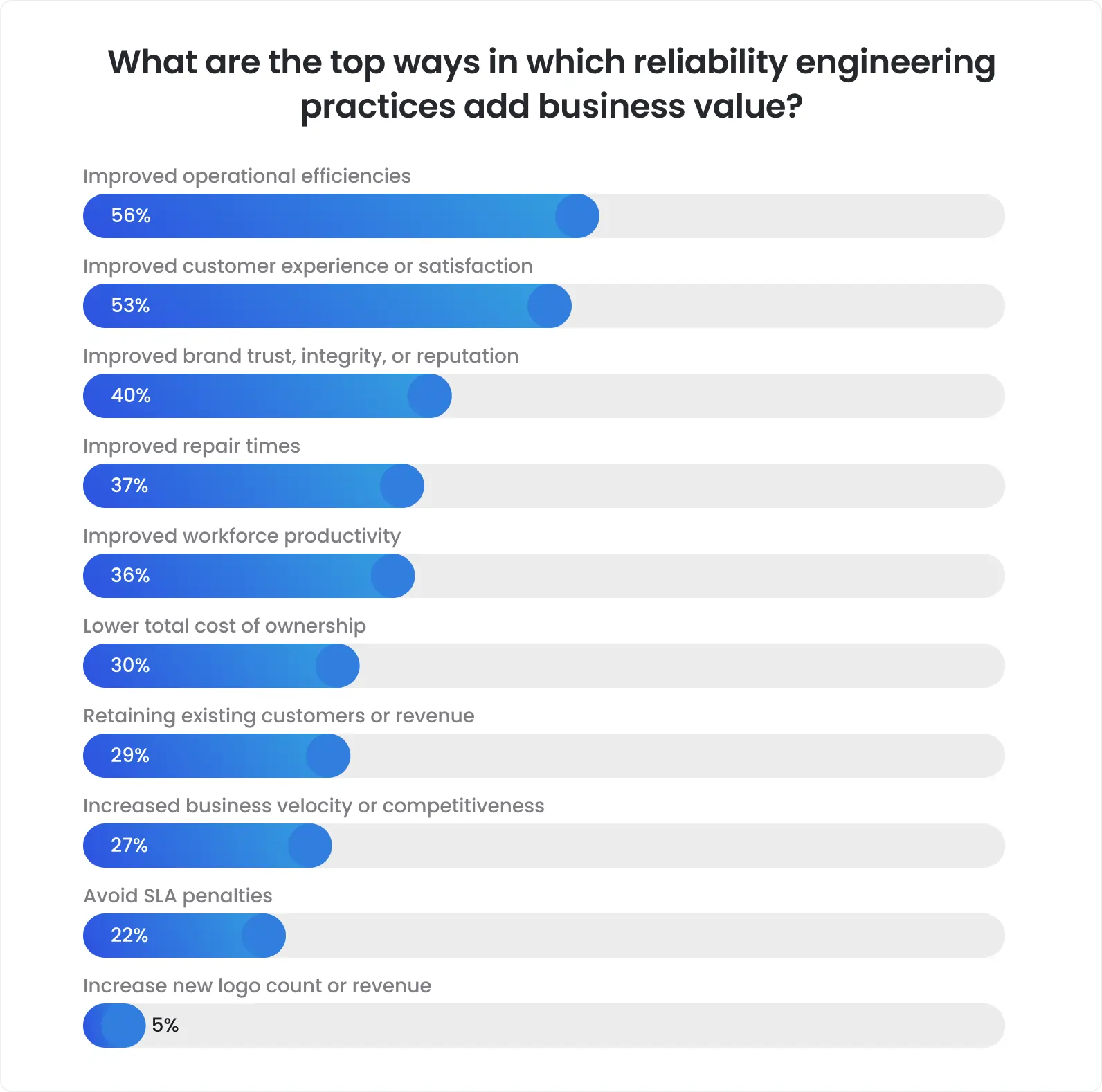
Yet, there is an opportunity to go beyond usual DevOps, and many companies will do this in 2025 by adopting QAOps. As you might guess, this approach actually implies adding one more ingredient to DevOps - QA.
Automated software testing is integrated directly into the CI/CD pipeline, while development, operations, and QA teams closely collaborate on achieving a common goal - delivering software of excellent quality.
Knowing the great capabilities of automated testing on its own, just imagine what outstanding results it can bring while being introduced into the DevOps environment! Faster time to market, better software quality, optimized collaboration, cost savings, and better user experience are just a few of the numerous benefits of QAOps that make it so attractive for companies in 2025.
Trend 2: Shift-left and shift-right testing

Probably, you’ve already heard about shift-left testing as it represents one of the golden rules of quality assurance – the earlier testing is started, the more time, money, and effort are saved. A well-known IBM study has shown that bugs detected post-production or after release usually cost 15 times more to fix compared to ones resolved at the early stages of software development. This, as well as better software quality, explains the popularity of this approach.
Trend 3: AI and automation
Let’s face the truth – AI is taking the world by storm, and it would be inexcusable not to highlight AI and automation among new trends in software testing. With its impressive capabilities, like machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, computer vision, etc., AI takes test automation to the next level, making things that used to be impossible possible and speeding up the testing process dramatically.
46% of respondents have already integrated AI technology into their QA efforts, and surely more will follow this practice in 2025.
QA areas revolutionized by AI adoption:
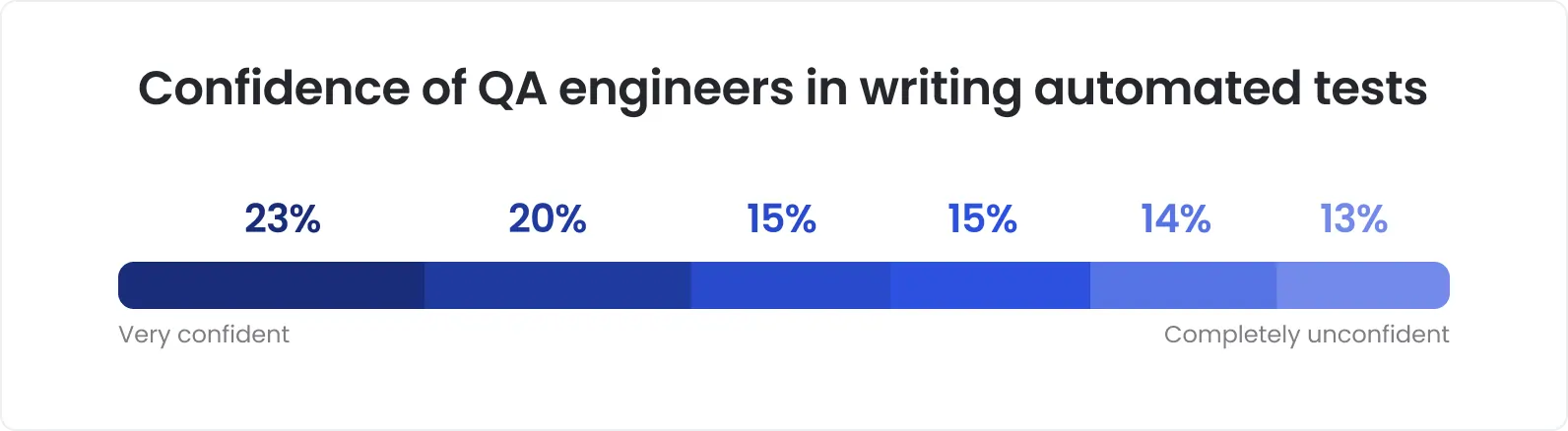
If the previous point didn’t impress you, hold on – AI-based testing tools now enable the automated development of test scripts in any programming language. Moreover, generated test suites are kept relevant and updated as AI algorithms detect changes in the app code and automatically adjust test scripts accordingly. This is of utter importance as only 23% of QA engineers are confident in writing automated tests.
Confidence of QA engineers in writing automated tests
AI algorithms are heavily used to create synthetic testing data automatically. This saves time and enables comprehensive testing without compromising on sensitive data. 14% of teams introduce AI for efficient test data management.
Upon identifying changes made to app code and areas most prone to errors, AI tools select the most critical tests to be run, which saves a lot of time and resources.
Trend 4: Site reliability engineering (SRE)
Site reliability engineering has a goal to improve the reliability of software systems as well as to maintain their high performance and availability by using principles and practices that integrate software engineering with IT infrastructure and operations. That’s where SRE resembles DevOps in a certain way.
Site reliability engineers handle performance tuning, fault diagnosis, infrastructure management, system monitoring, process documentation, capacity planning, and prevention of future issues based on previous system failures.
While certain SRE practices can be performed by regular employees, more companies eventually hire dedicated specialists for this job.
According to Catchpoint, on average, in 30% of companies, post-incident work is led by SREs, which highlights the growing popularity of this discipline.
Trend 5: Cloud testing
Cloud testing is poised to become a significant trend in 2025, driven by the increasing adoption of cloud technologies that ensure speed, scalability, and global accessibility.
According to Marketsandmarkets, the global cloud-native app market was valued at 5.9 billion USD in 2023, but it is expected to reach 17 billion by 2028.
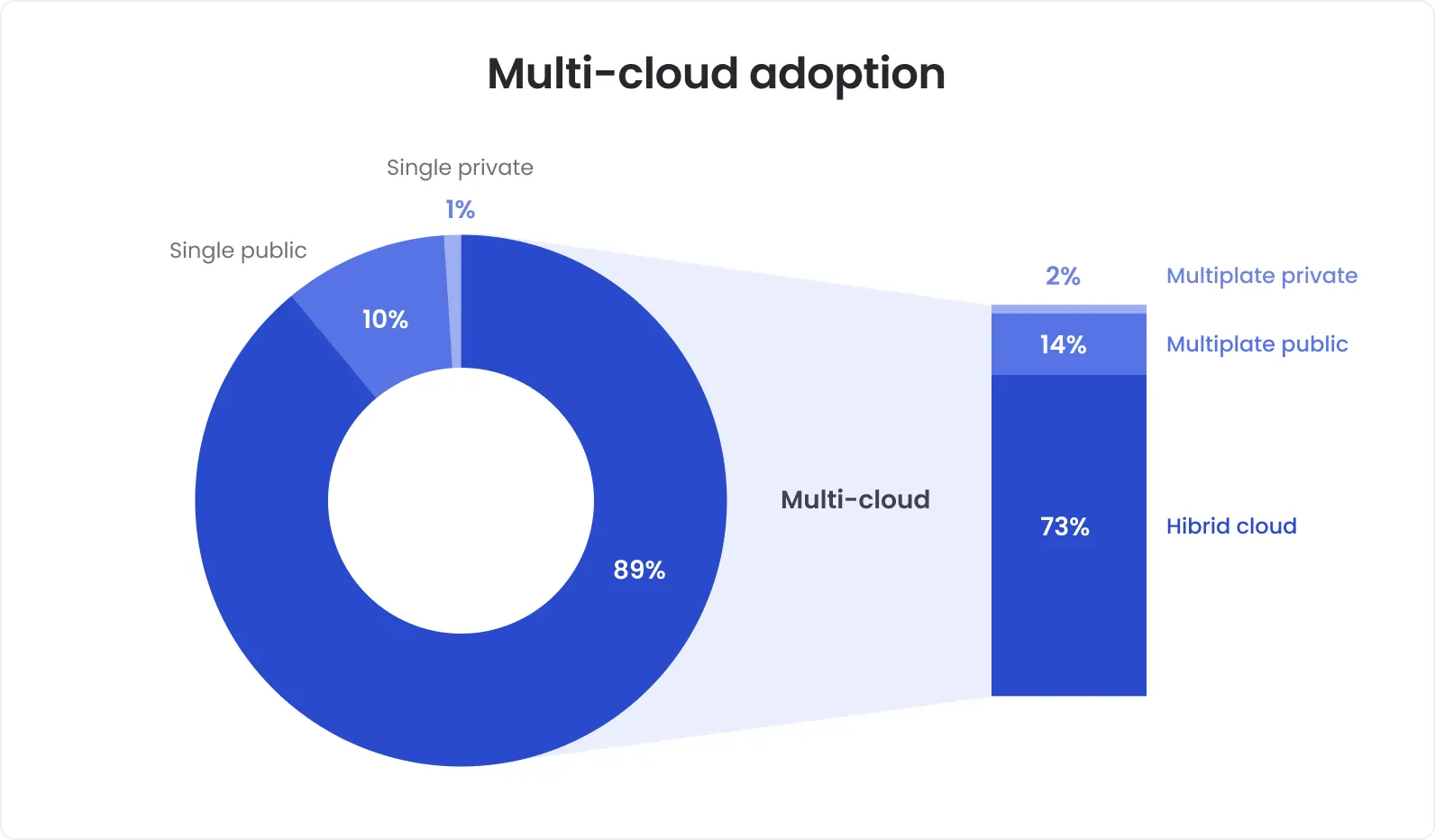
Active adoption of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments is one more important factor fostering demand for cloud testing.
Multi-cloud adoption
Trend 6: IoT and phygital testing
One more trend in software testing that deserves attention is IoT testing. Thanks to the expansion of 5G and advancements in data analytics powered by AI and ML, IoT applications vary from usual smartwatches to complex smart cities. Besides, nowadays, companies across diverse industries strive to provide phygital experience, i.e. a blend of digital and physical experiences, and this also fuels IoT development.
Statista reports that the global number of enterprise IoT connections will reach about 24 billion by 2030.
Taking into consideration all these facts, we’ll definitely notice a higher demand for IoT testing services, and you should be ready for this. In 2025, IoT testing will need to address the unique challenges related to highly interconnected ecosystems. QA experts will deal with hardware variations, numerous protocols, and real-time data flows. Also, ensuring security, reliability, and performance across diverse IoT environments will necessitate the refinement of specialized testing strategies.
Areas to pay attention to:
While thriving across diverse domains, the Internet of Things has been particularly impacting the following areas:
Smart homes
Healthcare
Industrial IoT
Smart cities
Agriculture
Transportation and logistics
Environmental management
Trend 7: Security testing
Cybercriminals are on the watch, and cyberattacks are getting more intensified and sophisticated. Zero-day vulnerabilities, DDoS attacks, bot traffic, and other threats keep on bothering companies of all kinds and sizes.
Deloitte Cyber Survey revealed that 40% of respondents reported 6 to 10 cybersecurity breaches last year. Meanwhile, 53% of companies lack confidence in their app security.
Solid protection of software systems against attacks requires a proactive approach to security flaw identification, which makes security testing a must. In 2025, security testing will no longer be a separate activity but rather a core component of the QA process.
Vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and compliance testing will be actively integrated into the development lifecycle while teams practicing DevOps will switch to DevSecOps.
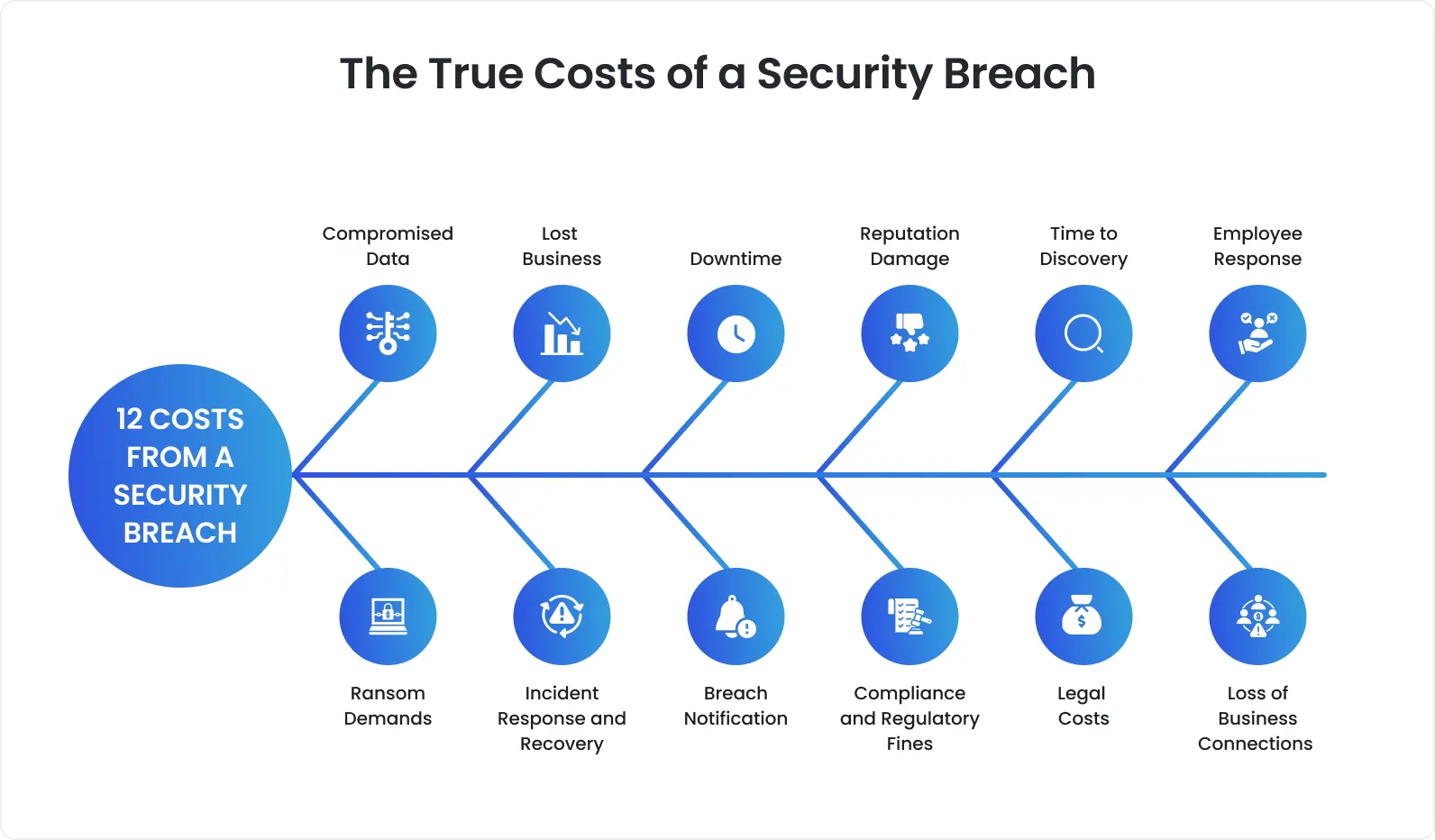
Key types of security testing to execute:
Vulnerability scanning suggests the automated running of tests that check apps and networks for security flaws and weaknesses that can expose them to threats.
Pen testing is particularly interesting and beneficial. It is carried out by ethical hackers who spot and exploit weaknesses within a system to assess the level of risk they impose and offer efficient mitigation strategies.
Security posture assessment evaluates a system's ability to withstand diverse cyber threats through the execution of various security testing methodologies.
Risk assessment is conducted with the goal of identifying and prioritizing security threats for a company or project and recommending relevant measures for risk reduction.
Trend 8: Performance testing
A few years ago, Google revealed stats that 53% of visits are likely to be abandoned if pages take longer than 3 seconds to load. Since then, apps have become more complex and users more demanding – they expect lightning-fast experiences. So, while evolving, performance testing remains among the current trends in software testing.
Trend 9: Usability and accessibility testing
Usability is as important as never, because apps need to be intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable to withstand severe competition.
Besides, did you know that about 1.3 billion people experience disability? This represents 16% of the world’s population.
So top-notch software development companies strive to build user-friendly and accessible solutions that cater to various social groups, demographics, and users with different technical literacy levels. The growing role of both usability and accessibility testing lets us include them in the list of top software testing trends in 2025.
Trend 10: Sustainability in testing
Have you heard something about green testing? This is the last but very interesting trend we’d like to outline.
As a part of a large movement towards sustainable IT practices, green testing aims to decrease the environmental impact of software testing, mostly through smart energy consumption and resource usage.
With over 15 years of expertise in software testing services, DeviQA leverages the latest testing technology to align with your project’s unique requirements, delivering industry leadership, efficiency, cost savings, and superior quality.