26 minutes to read
Top automation testing tools of 2025


Anastasiia Sokolinska
Chief Operating Officer
Summarize with:
Straight to the point: 26% of companies have trouble selecting the right tools, and as a result, most teams don’t use automation to its full potential and only 12% of software development teams automate more than 75% of their testing.
The right automation testing tools can fix this. The wrong ones slow you down.
Here’s a list of the top automation testing tools for 2025 — what they do, why they stand out, and how they can fit into your workflow.
By the end of this article, you'll have a better idea of which tool fits your needs best.
What are test automation tools?
Test automation tools are software that test other software applications. They make sure the applications work correctly and meet specific requirements. These tools can handle different tests, like checking if features work, how fast the software runs, if old stuff still works after updates, or if it’s secure.
They spot bugs and problems early, so developers can fix them before things get messy. You set them up with instructions, and they run the tests automatically — faster and more reliably than doing it by hand. They’re a big help for repetitive or complex jobs.
Here are the key benefits of using QA automation tools:
Top 14 automation testing tools
So, how’d we pick the top automation testing tools for 2025? We looked at what really matters: tools that handle a mix of testing needs, feel approachable no matter your skill level, play nice with your dev setup, have a strong community (or solid backing), and bring something fresh — like AI smarts or cloud power. Here’s our list of the top test automation tools you’ll want on your radar.
1. Playwright
Playwright, developed by Microsoft and released in 2020, has solidified its position as a top automation testing tool. It’s like an upgraded version of Selenium with extra powers. Built for modern web applications, it offers a unified API to automate Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit browsers. Its focus on reliability, speed, and cross-browser testing makes it a strong contender for teams tackling complex, dynamic interfaces.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Unified API for all major browsers (no need to write browser-specific code); - Strong support for modern web technologies (iframes, file uploads, geolocation testing, etc.); - Fast execution and low flakiness, thanks to built-in waits and retries, make it one of the best automation tools for teams requiring stability; - Excellent parallel test execution support, both locally and in the cloud; - Active development and regular updates from Microsoft; - Built-in tracing, screenshots, and video recording for better debugging. | - Slightly larger learning curve compared to Cypress (more configuration needed) - Newer than Selenium - smaller ecosystem (fewer third-party integrations than Selenium) - Focused primarily on web testing - does not cover native mobile apps (unlike Appium) - Debugging across multiple languages (if teams mix Python, JavaScript, etc.) can be challenging |
Best use cases:
2. Appium
Appium is a leading open-source test automation tool designed specifically for mobile application testing. In 2025, it remains a top choice for teams that need to automate testing across iOS, Android, and even Windows desktop apps. Built on the philosophy of “write once, test anywhere,” Appium allows testers to reuse the same test scripts across platforms, saving time and effort in cross-platform mobile automation.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - A single framework for both Android and iOS automation. - Large community with strong open-source support. - Compatible with a wide range of top automation testing tools (like TestNG, JUnit, Mocha, etc.). - Supports real devices, emulators, and simulators. | - The initial setup can be complex, especially for beginners. - Execution speed tends to be slower compared to some newer AI-driven or native automation QA tools. - Debugging issues across platforms can be tricky due to differences in iOS and Android behaviours. - Limited support for some advanced gestures or OS-level interactions on certain devices. |
Best use cases:
3. Cypress
Cypress is one of the most developer-friendly automation testing tools, especially for modern web applications. Unlike traditional software testing tools like Selenium, Cypress runs directly in the browser, offering fast test execution, easy debugging, and a smooth user experience. In 2025, it continues to be a popular choice for agile teams, particularly those focused on JavaScript-heavy applications and component testing for modern front-end frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Easy setup and quick learning curve, even for teams new to automated testing tools. - Seamless integration with JavaScript-based projects. - Great documentation and active community. - All-in-one software test automation tool (no need to configure extra reporters, runners, etc.). - Excellent error reporting with clear stack traces and screenshots/videos. | - Only supports Chromium-based browsers (Chrome, Edge) + Firefox and WebKit (still evolving) — limited cross-browser support compared to Selenium. - Limited support for multi-tab and multi-origin scenarios. - Primarily designed for web apps — not suitable for mobile or desktop app testing. - Tight coupling with the JavaScript ecosystem — less ideal for teams working in other languages like Java or Python. |
Best use cases:
4. Selenium
Selenium remains one of the best automation testing tools in 2025. It’s like a robot that can click buttons, fill out forms, and check web pages for you. Known for its versatility and robust community support, Selenium is an open-source framework designed primarily for web application testing. It supports multiple programming languages, browsers, and platforms, making it a go-to choice for teams looking for flexibility in their test automation strategies.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Large community support and extensive documentation. - Completely free and open-source. - Highly flexible and customizable test automation tool. - Supports both local and cloud-based execution (via platforms like BrowserStack or Sauce Labs). | - No built-in reporting or test management features — requires third-party tools. - Steeper learning curve for beginners compared to codeless software testing tools. - Primarily focused on web testing — not suitable for a mobile app or desktop app automation without additional tools (like Appium or WinAppDriver). |
Best use cases:
5. Katalon Studio
Katalon Studio is an all-in-one software testing tool that automates web, mobile, API, and even desktop apps. Its combination of record-and-playback functionality, built-in templates, and support for scripting makes it a top test automation tool for both manual testers transitioning to automation and experienced engineers.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - An all-in-one platform covering multiple test types (UI, API, mobile, desktop). - Suitable for both technical and non-technical testers, lowering the barrier to using software automated testing tools. - Rich set of built-in keywords, reducing time spent on creating basic test actions. - Strong integration with popular tools like Jira, Git, Jenkins, and Slack. - Active development and clear documentation, with regular updates. | - Limited programming language options (Groovy only for scripting), which may restrict flexibility for teams preferring Python, JavaScript, or other languages. - Resource-intensive for large test suites, especially when running in parallel. - Commercial licensing — while a free version exists, advanced features are only available in the paid version. - Customization limits — some complex scenarios may require workarounds or integration with external libraries. |
Best use cases:
6. TestComplete
TestComplete, developed by SmartBear, remains one of the most mature and feature-rich automated software testing tools. Known for its broad application support, TestComplete enables UI test automation across desktop, web, and mobile applications. Its scripted and scriptless (keyword-driven) options cater to both technical testers and manual testers adopting test automation tools.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Broad technology support, covering web, desktop (including older Win32 apps), and mobile. - Supports multiple scripting languages, giving teams flexibility in how they write tests. - Advanced object recognition handles dynamic elements well, reducing test flakiness. - Extensive reporting and audit-friendly logs. - Easy onboarding for manual testers through keyword-driven and record-and-playback capabilities. | - Requires a paid license, which can be expensive for smaller teams. - Heavier footprint compared to lighter software testing tools like Cypress or Playwright. - Primarily Windows-based — lacks first-class support for macOS/Linux, limiting options for cross-platform testers. - The learning curve can be steep for teams aiming to maximize scripted automation. |
Best use cases:
7. Ranorex Studio
Ranorex Studio is a comprehensive test automation tool known for its user-friendly interface and powerful automation capabilities across web, desktop, and mobile applications. Designed to bridge the gap between manual testers and automation engineers, Ranorex offers codeless automation alongside the flexibility to enhance tests with code using C# or VB.NET. In 2025, Ranorex remains a strong choice for teams needing a QA tool with robust object recognition combined with enterprise-grade reporting and cross-platform automation.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Comprehensive technology support, including web, desktop, and mobile. - Strong object identification even for dynamic and custom controls. - Codeless automation lowers the barrier to entry for manual testers. - Customizable reports with rich details like screenshots and logs. - Mature and reliable software test automation tool, backed by strong community and professional support. | - Paid tool, with licensing costs that may be high for smaller teams. - Windows-centric — While web and mobile testing supports various platforms, the Ranorex Studio IDE itself only runs on Windows. - Heavier footprint compared to lightweight browser-based top automation testing tools like Playwright or Cypress. - Teams exclusively testing modern web apps may find more agile options like Cypress or Playwright more attractive. |
Best use cases:
8. JUnit
JUnit is one of the most widely used test automation tools for unit testing in Java projects. Though primarily designed for unit testing, JUnit is also adapted for integration and functional testing in many Java-based applications. Its lightweight nature, ease of integration into CI/CD pipelines, and compatibility with popular development tools make it a staple for teams building software with Java, Kotlin, or other JVM-based languages.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Lightweight, fast, and ideal for rapid feedback in fast-paced projects. - Fully integrated into the Java ecosystem, with strong support in IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA and Eclipse. - A large, active community offering extensive documentation and support. - Flexible and adaptable to various testing styles. - Free and open-source, cost-effective for teams of all sizes. | - Not suitable for non-Java projects, limiting its versatility compared to other software test automation tools. - Primarily designed for unit tests, so teams doing end-to-end (E2E) or cross-platform testing will need to combine it with other tools. - Limited built-in reporting — Requires additional plugins or frameworks to generate rich reports. |
Best use cases:
9. TestNG
TestNG (short for "Test Next Generation") is a popular automation software testing tool for Java applications, designed to overcome some limitations of JUnit and offer more powerful testing capabilities. It supports a wider range of test types, including unit, integration, functional, and end-to-end tests, making it a versatile choice for modern Java projects in 2025. With advanced configuration options, flexible test execution, and robust reporting features, TestNG continues to be a go-to test automation tool in complex projects.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - More powerful than JUnit, offering greater flexibility in test grouping, dependencies, and parameterization. - Built-in parallel execution speeds up large test suites, a major advantage in automation tools. - Clear, configurable reports help teams analyze results faster. - Strong ecosystem support with native integration into Maven, Gradle, and popular IDEs like IntelliJ and Eclipse. - Ideal for both unit and functional tests, making it a one-stop framework for many projects. | - Steeper learning curve compared to JUnit, especially for beginners. - Java-only — Like JUnit, it’s not suitable for non-Java projects. - Advanced features like test dependencies and parallel runs require careful configuration, which can be error-prone in complex environments. |
Best use cases:
10. Postman
Postman has evolved far beyond being just an API test automation tool. In 2025, it stands as a comprehensive API platform that supports designing, testing, automating, and monitoring APIs. Known for its user-friendly interface and powerful automation capabilities, Postman allows teams to write and execute automated tests for REST, SOAP, and GraphQL APIs, making it the top automation testing tool for API-first development and microservices testing.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - User-friendly interface, making it accessible for testers, developers, and non-technical stakeholders alike. - All-in-one API platform for designing, testing, and monitoring APIs. - Extensive documentation and community support. - Flexible test scripting using JavaScript, familiar to most developers. - Free and paid versions — Flexible enough to fit both startups and enterprises. | - Limited to backend testing; no UI or mobile automation capabilities. - Advanced monitoring and parallel runs require paid plans (e.g., Postman Enterprise). - Can slow down with large collections or heavy scripting, automation testing tools like JMeter offer more robust performance/load testing features. |
Best use cases:
11. Robot
Robot is an open-source test automation tool primarily used for acceptance testing and robotic process automation (RPA). Known for its keyword-driven testing approach, Robot enables non-programmers to easily write test cases, making it a popular choice for teams with varied skill sets. In 2025, the tool has evolved to support a wide range of test automation tasks, from web testing with Selenium to API testing and database testing, thanks to a rich ecosystem of libraries and tools that extend its functionality.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Readable test cases through a keyword-driven approach, ideal for non-technical users. - Extensive library support for various testing needs and easy customization. - Open-source with no license fees, constantly improved by the community. - Platform-independent works across multiple operating systems. - Extensible with custom keywords and integrations like Selenium and Appium. - An active community offering tutorials, plugins, and integrations. | - Slower execution compared to code-driven top automation testing tools like JUnit or TestNG. - Less ideal for unit testing, better suited for high-level testing. - Limited UI testing support, not as optimized as tools like Cypress. - The learning curve for advanced features like parallel execution and complex integrations. |
Best use cases:
12. Applitools
Applitools is a visual testing platform that specializes in automated visual validation of web and mobile applications. By using AI-powered visual AI and visual regression testing, Applitools helps teams detect and fix visual bugs and ensure that the UI appears correctly across various browsers and devices. This automated QA tool is particularly useful for teams that need to guarantee that any visual discrepancies caused by code changes, browser variations, or device differences are promptly identified.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - AI-powered visual testing provides accurate and efficient UI validation. - Cross-browser compatibility ensures consistent visual appearance across different browsers. - Cloud-based eliminates infrastructure maintenance needs. - Easy integration with popular QA testing software tools like Selenium and Cypress. - High-speed testing with parallel execution, saving time on large test suites. | - Limited focus on functional testing — Applitools is primarily focused on visual testing, so functional testing may need other tools. - Pricing can be higher compared to other QA testing tools due to its premium features. - The learning curve for users unfamiliar with visual testing principles or AI-based tools. |
Best use cases:
13. BrowserStack
BrowserStack is a cloud-based cross-browser testing platform that allows developers to perform manual and automated testing of web and mobile applications on real devices and browsers. It provides an easy-to-use, scalable solution to test applications across different operating systems, browsers, and devices without the need for local device setups or virtual machines. BrowserStack supports integration with top automated testing tools like Selenium, Cypress, Appium, and more.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Extensive browser/OS matrix (e.g., Chrome 120, Safari 18, Android 14) ensures thorough testing. - Cloud infrastructure eliminates local setup and boosts parallel execution. - Features like SSO, IP whitelisting, and detailed analytics cater to large teams. | - Subscription-based pricing starts at $39/month for individuals; enterprise plans (~$199+/month) are needed for full features. - Relies on internet connectivity; offline testing isn’t an option. - Configuring advanced setups (e.g., local testing via BrowserStack Local) can be tricky. |
Best use cases:
14. testRigor
testRigor is a modern AI-powered test automation tool designed to simplify test creation and reduce test maintenance efforts. It supports web, mobile, and API testing and allows testers to write plain English test scripts, positioning it among the top software automated testing tools for accessibility and efficiency. With its focus on no-code automation and self-healing tests, testRigor helps teams accelerate test coverage without requiring deep programming expertise.
Key features:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Plain English tests lower the barrier for non-technical users. - Self-healing minimizes flaky tests and reduces maintenance. - End-to-end coverage across web, mobile, and APIs. - AI-driven test suggestions speed up test suite creation. - Seamless CI/CD integration supports modern delivery workflows. | - Limited advanced customization compared to code-centric test automation tools like Selenium or Playwright. - Pricing can be higher than traditional open-source QA tools. - Reliance on AI may not always handle complex, highly customized workflows effectively. |
Best use cases:
What to consider when choosing a test automation tool?
Selecting a test automation tool can feel overwhelming. Choose right, and testing gets smooth and reliable. So how do you decide? It depends on your project, team, and goals. Here’s a clear breakdown of what to think about.
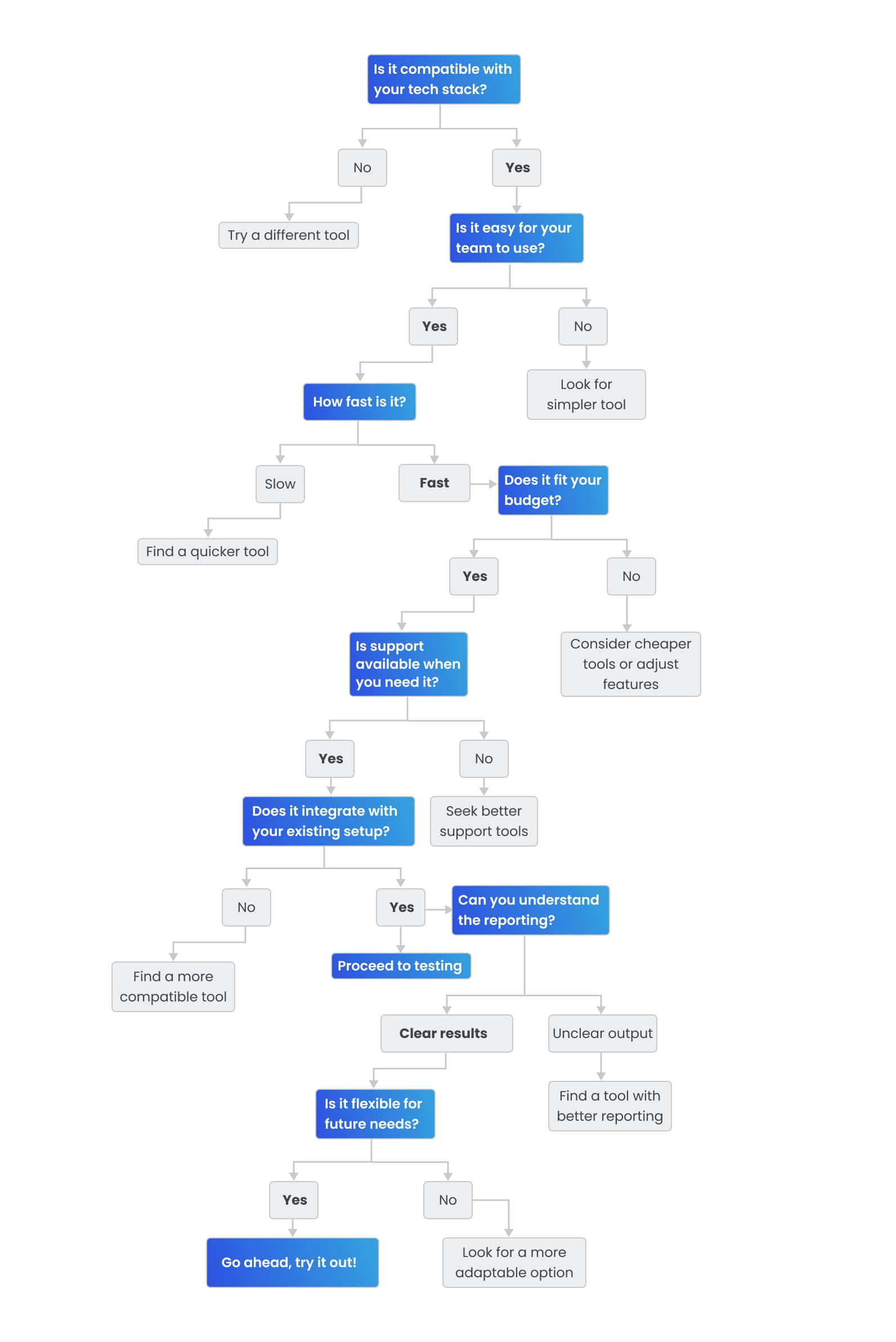
That’s the list. Hit these points, and you’ll pick the best automation tool solid. No tool’s perfect, but you can find one that’s good enough.
Conclusion
Here’s the deal: In 2025, automation testing tools are all over the place — from trusty open-source champs like Selenium and Appium to slick AI-powered options like testRigor and Applitools. Whether your priority is robust cross-browser testing (Playwright), comprehensive mobile app support (Appium), precise visual validation (Applitools), or an integrated all-in-one solution (Katalon Studio), there’s a test automation tool suited to your objectives.
Consider key aspects:
Then test your shortlist with real-world scenarios through trial periods. The goal isn’t to find a flawless option but to identify a practical fit that meets your team’s current needs and adapts to future demands.
Make the right call, and automation becomes a strategic advantage, enhancing software quality and operational efficiency with confidence.
Need help choosing the right automation testing tool for your project?
With so many options available, selecting the best-fit tool for your tech stack, project goals, and team skills can be challenging. Our experienced QA consultants can help you evaluate your requirements and recommend the most efficient, cost-effective, and future-proof test automation tool for your business. Schedule a consultation today and make confident decisions for your testing strategy.
Similar Posts

5 minutes to read
Top 7 AB Testing Tools That You Should Use in 2025
- Mobile App Testing Tools
- Android App Testing Tools
- Mobile App Automation Testing Tools
- App Testing Tools
- iOS App Testing Tools

12 minutes to read
Best Cross Browser Testing Tools in 2025
- Cross Browser Tools
- Cross Browser Testing
- Tools for Testing Browser
- Cross Browser ToolsReview

7 minutes to read
Best Cloud Testing Tools
- Cloud Testing
- QA Tools
